SARs are a type of equity-related compensation given to employees. It is a cash bonus that equals to an increase in the value of a company's stock over a predetermined period. SARs are often used as an incentive to motivate and retain employees. In this article, we will discuss the benefits of SARs for private companies, how they work, compare them to other equity compensation assets and explain why they are not for everyone.
What are Stock Appreciation Rights?
Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs) are equity-based employee compensation that allow employees to benefit from the appreciation of their company's stock price. The compensation is equal to the increase in stock price during a particular period for a pre-specified number of shares. SARs plan are flexible and can be easily customized. It allows employers to use them as a tool for incentivizing and retaining each individual member of the team.
SARs are often granted to employees in addition to their regular salary or as an alternative to traditional stock options. But it is not uncommon for companies to offer SARs “in tandem” with stock options. In case of a combination of the two, employees get access to funds to cover exercise costs of stock options using the benefits gained from SARs payments.
SARs vs Stock Options
SARs are different to traditional stock options. In the case of the latter, employees exercise their right to buy company's shares. SARs do not require employees to purchase any stock. SARs entitle recipients to benefit directly from the appreciation of their company’s equity without having to pay any up-front cost. SARs provide employees with cash or, in rare cases, stock equivalent to the increase in the value of the company's stock.
SARs vs Phantom Shares
Stock appreciation rights and phantom shares are very similar. The two don't guarantee real equity but rather a monetary compensation that is linked to the stock's price growth. However, the recipients of phantom shares are either entitled to the value of the company's shares (full value) or the increase that happens (appreciation only). And phatom shares plans are often linked to liquidity events such as an acqusition, IPO, funding round. At the same time, SARs allow its recipients to obtain a right to the monetary benefit related to the growth of the stock price of granted shares over a specified period of time.
How do Stock Appreciation Rights Work?
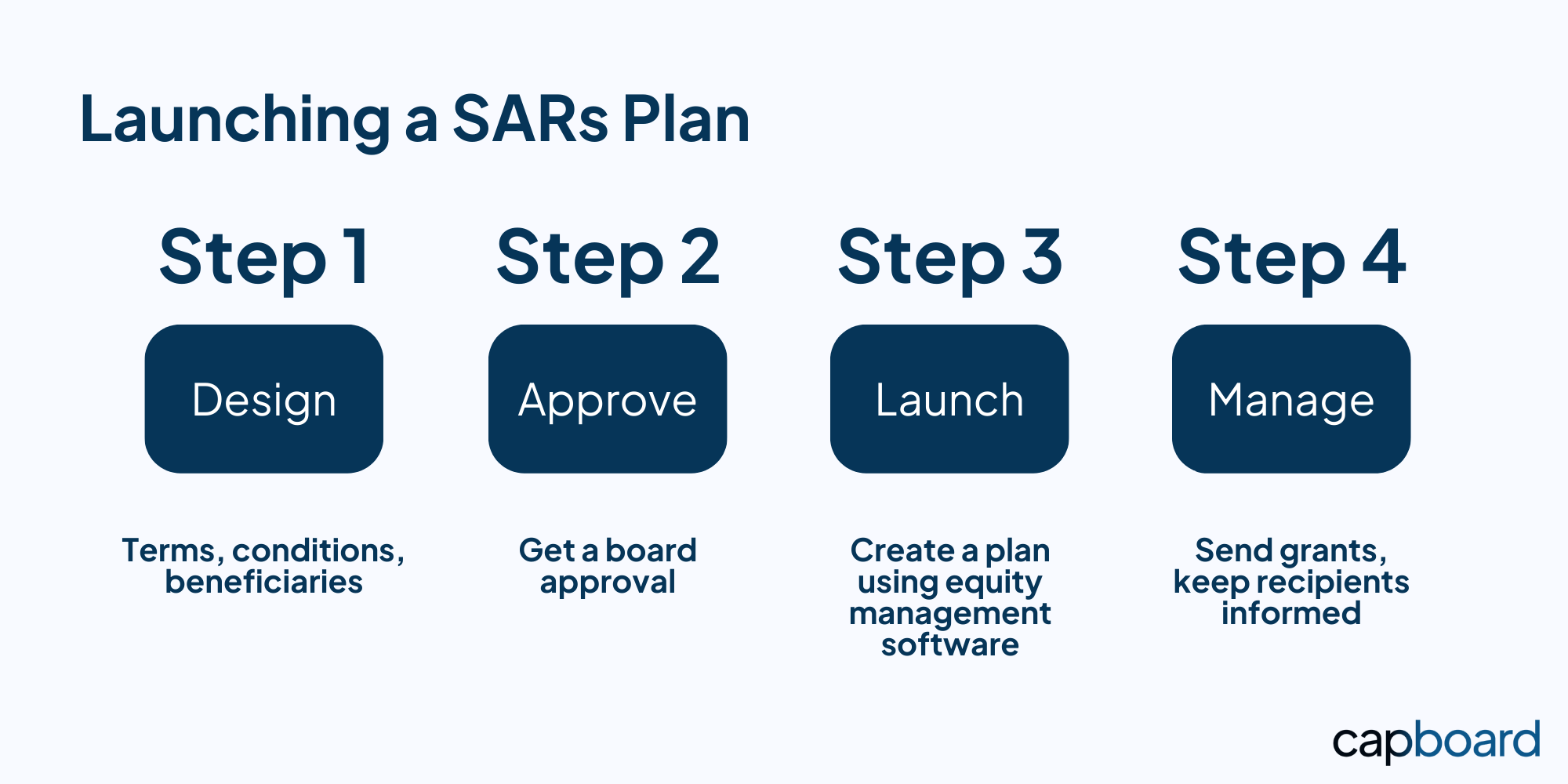
Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs) are a popular form of equity-related compensation among private companies and startups. Here is how a Stock Appreciation Rights plan actually works:
- Board approval: To implement a SARs program, the company's board of directors needs to approve the plan. It involves deciding on the eligible employees based on factors such as their role, performance, and tenure.
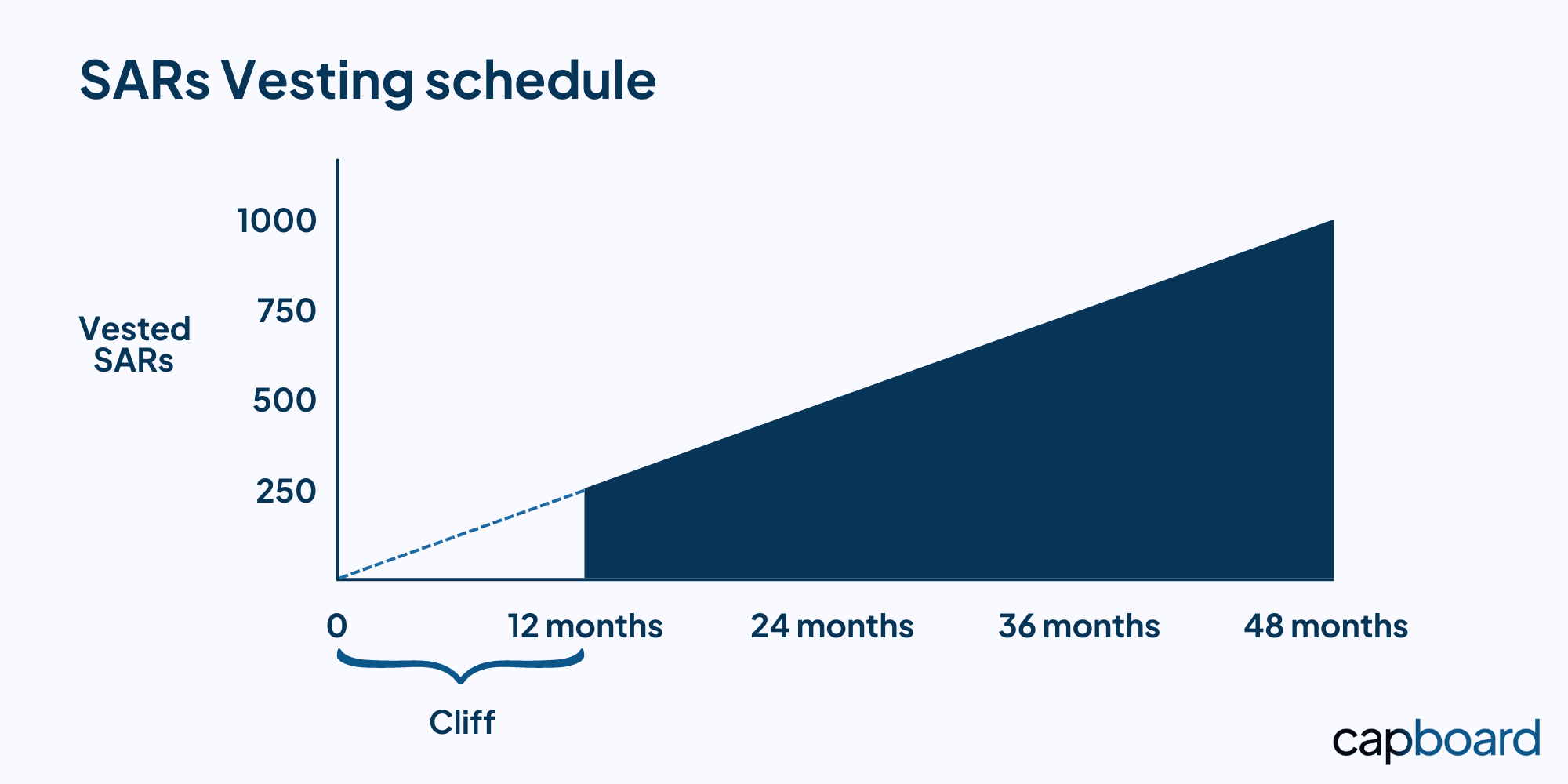
- Stock appreciation rights vesting: SARs typically vest over a period of 3-5 years. Given the flexibility of the plan, you can set the vesting schedule and plan terms on an individual level. It will allow you to align the program's goals with those of each employee, making sure they are satisfied.
SAR liquidity:
- Employee calls the shots: Under some circumstances, the employee can be the one deciding when to exercise their SARs (given the plan's terms and schedule). When the employee exercises, they receive a cash payment equal to the increase in the stock value over the price at the grant date. This payment is subject to taxes and other withholdings.
- Employer decides: Under other circumstances, the agreement can specify that the exercising will happen at a future date or at a pre-defined event. At this moment, the company will do a valuation of the stock to determine the change in price. In case of an increase, the employee will receive a payment.
- Exit scenario: In the event of an exit, such as a merger&acquisition or an IPO, the SARs may become fully vested. In that case, the employee will receive a cash payment equal to the increase in the stock value since the grant date.
Overall, SARs can be a valuable tool for private companies and startups to reward and retain employees. However, it's important to carefully design and organize the program to align with overall compensation goals and strategies.
Stock Appreciation Rights Example
As a part of a simple example, let's say a company grants an employee 100 SARs at a moment when the stock price is at $10 per share. The vesting period is 4 years.
Now, let’s imagine that the company's stock price increases to $15 per share over the vesting period. When the terms of the plan are satisfied, the employee receives a payment of $500 (100 SARs x ($15-$10) per share).
SARs Benefits
- Cost-effective incentive: Startups often have limited cash flow. This does not allow them to compete with established companies in terms of salary and benefits. Offering SARs as a form of compensation can be a cost-effective way to hire and motivate key employees. But it’s important to remember that later on, after the SARs are vested the company may need to pay. If the stock price increases, the company will have to compensate the SARs recipients with cash.
- Aligning employee incentives with company goals: By granting SARs, startups can align employee compensation with the goals of the company. Vesting can be milestone-based or time-based. It allows flexibility and makes sure employees are incentivized to work towards increasing the value of the company.
- Motivation level: SARs can be used by companies as a motivation tool for employees. You can benefit from such a type of compensation by inspiring your team to focus on what matters - growing the company. Which, as a result, will increase the value of stock and their future compensation.
- Simpler cap table: if we compare offering stock options vs stock appreciation rights to employees, the cap table will be simpler in case of SARs. When granting stock options, employees that exercise their rights and acquire company’s shares become shareholders. And, in that case, become a part of your cap table.
- Worst case scenario is not that bad: In case of SARs, employees will never be ‘underwater’ - their compensation’s value can never go below zero. That means that the worst case scenario is they will get nothing. Such a situation will happen when the stock price either stays the same or decreases compared to the price when SARs were granted. However, employees may think differently and we will explain it later in this article.
Why are Stock Appreciation Rights not for Every Private Company?
The benefits of SARs for startups and private companies described above may have created a compelling story for this type of compensation. But it’s not all rainbows and unicorns, for companies or for employees. Here is why SARs are not for every private company:

- Complexity: SARs can be complex and difficult to understand for employees. This can lead to confusion and dissatisfaction. Having no or poor communication plan in place can put the program at risk of having a negative impact on the company and its culture.
- Cash flow demands: Unlike traditional stock options, SARs typically provide employees with cash rather than shares of the company's stock. This means that private companies need to have sufficient cash reserves to pay out SARs awards when exercised. While at the moment of granting SARs it may seem like a great idea, but when the time comes, somebody will still have to pay. And this can be a challenge for companies that are still in their growth phase.
- Regulatory compliance: SARs must adhere to a number of regulations and may be examined by the US Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Private businesses could face legal and financial risks if they lack the means or expertise to follow these requirements.
- Company culture: SARs may not align with the culture and values of every private company. Some companies may prefer to offer more traditional equity compensation plans or other types of incentives to their employees. For some founders, providing real ownership in forms of equity to their employees can be more important.
- High risk compensation: The compensation using SARs will depend on the company’s stock value growth. Given the worst case scenario when the company’s share value stays the same or goes down, no compensation will be received. No growth = no benefit. And that is something that some employees may not find attractive. Especially if they don’t believe in the company’s growth.
Considerations for SARs
With everything that was mentioned so far, here are the considerations to take in mind when deciding on the SARs compensation in your company:
- Taxation and legal: To make sure that the company's leaders are aware of all the implications of SARs, we recommend you to speak with legal and tax advisors. It is essential to take all required actions to be able to follow all relevant laws and regulations.
- Cap table: Settling the compensation agreement with SARs owners using cash means that recipients will not become shareholders. As was already mentioned, that’s not the case when stock option owners exercise their right. With stock options, recipient are able to acquire shares and become shareholders on your cap table. With SARs, employees will not become equity owners (unless stock compensation for the value of the increase is granted).
- Valuation: Companies offering SARs should also determine the fair market value of their stock to establish the base price for the SARs. Setting an official valuation for SARs compensation is key to staying compliant. Consulting with a valuation expert may be necessary to ensure that the price used to determine the compensation is correct.
- Communication and Education of Employees: Clear communication of the details of the SARs program and education of your employees on how the program works is critical. This can help to ensure that employees understand the potential benefits and are aware of any scenarios of the program. As a result of the transparency and clarity, they can be motivated to contribute to the company's success. Providing them with personal dashboards where they can have an overview of their compensation can be a great step to ensure clarity and transparency.
Make offering equity compensation easy with Capboard
An effective equity compensation program can inspire and keep your employees aligned with the long-term company goals. And setting up and managing the ideal equity plan does not have to be complicated and time-consuming.
Private companies worldwide use Capboard’s equity management tools to grant equity-related compensation to employees, provide them with personal dashboards to ensure transparency and allow much-needed visibility over their compensation.